Transaxles and transmissions transfer engine power to wheels. A transaxle merges the transmission and differential, typical in front-wheel-drive vehicles. Conversely, transmissions in rear-wheel drives often pair with a separate differential. Costs and maintenance differ by vehicle design.
Introduction
In the automotive world, two integral components often come to the forefront when discussing the powertrain – the transaxle and the transmission. These terms, while sometimes used interchangeably, serve different purposes in a vehicle’s design and functionality. Here, we’ll delve deep into their definitions and the primary reasons we distinguish between them.
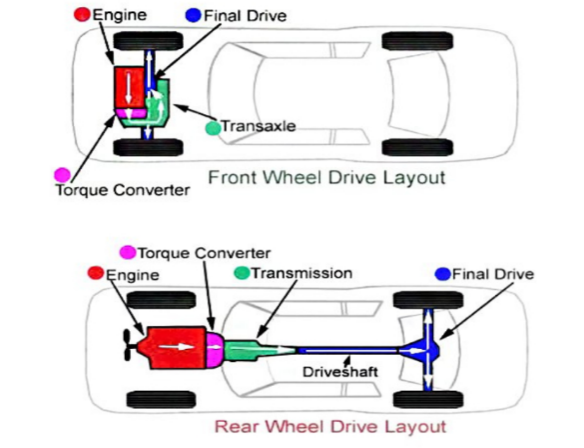
Definition of Transaxle
A transaxle is a single integrated unit that combines the functionalities of a transmission and a differential in front-wheel-drive and rear-engine vehicles. By merging these two components, automakers can save space and potentially reduce weight in specific vehicle designs. Its primary function is to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that vehicles move efficiently. For a comprehensive understanding, one can refer to Wikipedia’s detailed article on Transaxle.
Definition of Transmission
On the other hand, a transmission, commonly known as a gearbox, is a component that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source, like an engine, to another device, like the wheels. Its principal role is to adjust the power and torque sent to the wheels, ensuring optimal vehicle performance regardless of driving conditions. More information about transmissions can be found on Wikipedia’s Transmission page.
Purpose of Comparison
Given the pivotal roles both the transaxle and transmission play in a vehicle’s operation, it’s essential to distinguish their functionalities and applications. Not only does this comparison serve educational purposes for automotive enthusiasts and professionals, but it also aids consumers in making informed decisions when purchasing or maintaining vehicles.
Main Components and Functionality
Diving deeper into the realm of vehicles, it’s crucial to understand the underpinning components that make vehicles move. Two of the primary culprits in this domain are transaxles and transmissions. Beyond their definitions, knowing what constitutes these components and how they function is pivotal for both professionals in the industry and passionate car enthusiasts.
Key Components of a Transaxle
A transaxle is a marvel of engineering, integrating several crucial components:
- Gearbox: This consists of multiple gears that facilitate varying speeds and torque levels.
- Differential: This distributes engine torque to the wheels. Its primary function is to allow wheels to rotate at different speeds, especially crucial during turns.
- Final Drive: Responsible for the last stage of power transfer, it uses gears to transmit power from the gearbox to the differential.
Further details can be accessed on Wikipedia’s Transaxle page.
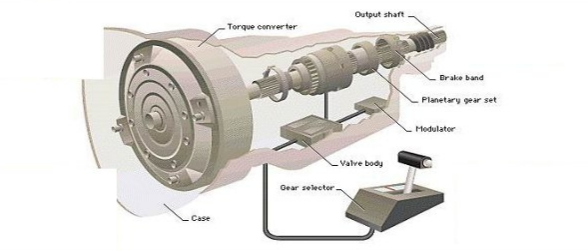
Key Components of a Transmission
The transmission, or the gearbox, is a slightly different beast. Its main components include:
- Input Shaft: This is the component that receives power from the engine.
- Output Shaft: This transmits the adjusted power from the input shaft to the vehicle’s wheels.
- Gears: They are responsible for the actual ‘transmission’ of power. They are available in varying sizes to provide different power and speed outputs.
- Synchros: These ensure smooth transitioning between gears.
For an in-depth dive into transmissions, Wikipedia’s Transmission page serves as an excellent resource.
How They Work
When it comes to functionality, both the transaxle and transmission are intertwined with a vehicle’s engine. As the engine produces power, it sends it forward to be modulated based on the vehicle’s needs.
In the case of the transaxle, the engine’s power first encounters the gearbox, where it gets adjusted based on the driver’s speed requirements. Then, the adjusted power is sent to the differential, which ensures that the torque is effectively distributed between the wheels.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The automotive world is replete with design choices, each bringing its set of benefits and challenges. When it comes to choosing between a transaxle and a transmission, understanding these pros and cons can lead to better decision-making, whether you’re designing a vehicle or simply buying one. Let’s dive into the advantages and disadvantages of both systems.

Benefits of Using Transaxle
Transaxles offer several compelling advantages:
- Space Efficiency: By integrating the transmission and differential into one unit, designers can save a significant amount of space, ideal for compact and sports cars.
- Weight Distribution: With the combination of major components in one location, transaxles can help in achieving better weight distribution, enhancing vehicle balance and handling.
- Fuel Efficiency: Due to reduced drivetrain power loss, vehicles with transaxles might offer better fuel efficiency in certain configurations.
For more insights, check out the advantages section of Wikipedia’s Transaxle page.
Drawbacks of Using Transaxle
While transaxles have their perks, they come with certain challenges:
- Complexity: Integrating multiple systems into one component can make the design and manufacturing process more intricate.
- Maintenance Costs: A problem in one part of the transaxle can sometimes require the entire unit to be serviced or replaced.
- Limited Application: Transaxles are primarily used in front-wheel-drive or rear-engine vehicles, limiting their application in the automotive world.
Benefits of Using Transmission
Transmissions, being a staple in most vehicles, have their set of advantages:
- Versatility: Transmissions can be used in a wide range of vehicles, from front-wheel-drive to rear-wheel-drive, making them ubiquitous in the automotive industry.
- Customization: Given the diverse range of transmission types, from manual to automatic to continuously variable transmissions, there’s a transmission for every need.
- Reliability: Standalone transmissions, especially manual ones, have a reputation for reliability and long service lives.
For a deeper dive into the world of transmissions, visit Wikipedia’s Transmission page.
Drawbacks of Using Transmission
As with any system, transmissions have their set of disadvantages:
- Space Consumption: Separate components, like the gearbox and differential, can consume more space than an integrated system like a transaxle.
- Weight: Standalone transmissions can sometimes add extra weight to a vehicle, affecting its balance and fuel efficiency.
- Maintenance: While reliable, transmissions, especially advanced automatics, can be costly to repair or replace when they do malfunction.
Applications and Usage
When it comes to vehicles, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. The choice between a transaxle and a transmission isn’t merely technical but also influenced by the specific use-case scenario of the vehicle. By delving into where and why these components are used, one can better understand their importance in the automotive ecosystem.
Vehicles that Typically Use Transaxles
Transaxles find their footing primarily in:
- Front-Wheel-Drive Cars: Due to their integrated design, transaxles are ideal for vehicles where the engine and the drive wheels are at the same end, like most front-wheel-drive cars.
- Sports Cars: Certain rear-engine sports cars, like the Porsche 911, employ transaxles for better weight distribution, leading to improved handling and performance.
- Certain Supercars: Some supercars prefer transaxles for their compactness and the performance advantages they can offer.
More on this can be explored at Wikipedia’s Transaxle page.
Vehicles that Typically Use Transmissions
Transmissions, given their versatility, find usage in a broader range of vehicles:
- Rear-Wheel-Drive Cars: Many sedans, sports cars, and trucks with a rear-wheel-drive setup use standalone transmissions.
- Four-Wheel-Drive Vehicles: SUVs, off-roaders, and certain trucks designed for rough terrains typically employ transmissions to distribute power to all four wheels.
- Commercial Vehicles: Buses, heavy trucks, and certain industrial vehicles prefer transmissions for their proven reliability and ease of maintenance.
For further reading, visit Wikipedia’s Transmission page.
Factors Determining the Choice
Choosing between a transaxle and a transmission isn’t arbitrary. Several factors play a pivotal role:
- Vehicle Design: The layout and design of a vehicle play a significant role. For instance, compact cars where space is a premium might opt for transaxles.
- Performance Needs: High-performance vehicles, seeking optimal weight distribution and compactness, might lean towards transaxles.
- Cost Considerations: Transmissions, especially manual ones, can be more affordable to produce and maintain, making them a preferred choice for budget vehicles.
- Durability and Reliability: In scenarios where robustness and long service life are essential, like in commercial vehicles, transmissions might get the nod due to their track record.
Maintenance and Longevity
A vehicle’s performance, reliability, and longevity largely hinge on the care and maintenance of its critical components. Among these, the transaxle and transmission are paramount. Regular maintenance not only ensures a smoother driving experience but also increases the lifespan of the vehicle. Let’s break down what care these components demand and what longevity one can expect from them.
Maintenance Requirements for Transaxles
Given the integrated nature of transaxles, they have specific maintenance needs:
- Fluid Checks and Replacement: Transaxle fluid, similar to transmission fluid, requires periodic checks. Depending on the vehicle’s make and model, fluid replacement might be advised every 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
- Seal and Gasket Inspections: To prevent fluid leaks, it’s essential to ensure that seals and gaskets remain intact. Regular inspections can prevent minor issues from turning into significant problems.
- Differential Checks: Given that the differential is part of the transaxle, periodic inspections ensure optimal performance and longevity.
More maintenance details are available on Wikipedia’s Transaxle page.
Maintenance Requirements for Transmissions
Transmissions, given their standalone nature, come with their own set of maintenance guidelines:
- Transmission Fluid Change: For optimal performance, it’s generally recommended to change transmission fluid every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle type and usage.
- Filter Replacement: In automatic transmissions, the filter keeps contaminants from reaching the transmission fluid. Depending on usage, these filters may need replacement every 20,000 to 100,000 miles.
- Regular Inspections: Periodic checks for wear and tear, leaks, or other potential issues can prevent costly repairs down the line.
A detailed maintenance guide can be found on Wikipedia’s Transmission page.
Expected Lifespan and Durability
The lifespan of both transaxles and transmissions varies based on several factors, including maintenance, driving habits, and the specific make and model of the vehicle.
- Transaxles: With regular maintenance, many transaxles can last upwards of 150,000 miles. However, aggressive driving or neglect can significantly shorten this lifespan.
- Transmissions: Manual transmissions, when treated well, can often exceed 200,000 miles. Automatic transmissions, given their complexity, generally have a lifespan ranging from 100,000 to 200,000 miles, contingent on regular maintenance.
Transaxle vs Transmission Price
The financial aspect plays a crucial role in the decision-making process, whether it’s manufacturers designing vehicles or individuals considering replacements or upgrades. Here, we will delve into the typical cost ranges for both transaxles and transmissions, keeping in mind that these prices can vary based on brand, region, and vehicle type.
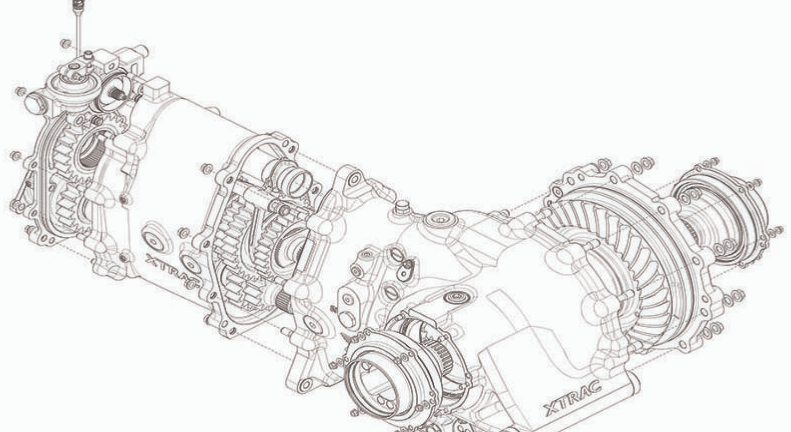
Cost of Transaxles
Transaxles, given their integrated design, have a unique price structure:
- New Transaxles: The price for a brand-new transaxle ranges from $1,500 to $3,500, depending on the vehicle type and brand. High-performance or luxury vehicle transaxles can be on the higher end of this range.
- Rebuilt or Remanufactured: Opting for a rebuilt transaxle might cost between $1,000 and $2,500. This range considers labor charges and the intricacy of the job.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular fluid changes can cost anywhere from $75 to $150, while significant repairs, such as replacing seals or addressing differential issues, might fall in the $500 to $1,500 range.
To delve deeper into the specifics of transaxles, Wikipedia’s Transaxle page is a valuable resource.
Cost of Transmissions
Transmissions, given their ubiquitous presence in the automotive world, have a varied cost spectrum:
- New Transmissions: A new transmission’s cost, depending on its type (manual or automatic) and the vehicle’s brand, can vary from $1,800 to $4,000. High-end vehicles or specialized transmissions can be pricier.
- Rebuilt or Remanufactured: A rebuilt transmission generally comes in between $1,200 and $3,000, taking into account labor costs and parts.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Routine transmission fluid changes might cost around $80 to $250, based on the fluid type and service quality. Major repairs, like replacing internal components, can range from $1,000 to $3,500.
It’s crucial to understand that these figures are ballpark estimates, and actual costs can vary. Local market conditions, labor rates, and parts availability can all influence the final price. Always seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough research before making financial decisions related to vehicle components.
