Most electric vehicles (EVs) do not have a traditional gearbox as they can operate efficiently across a wide range of speeds with a single-speed transmission.
Working Principle of an Electric Vehicle
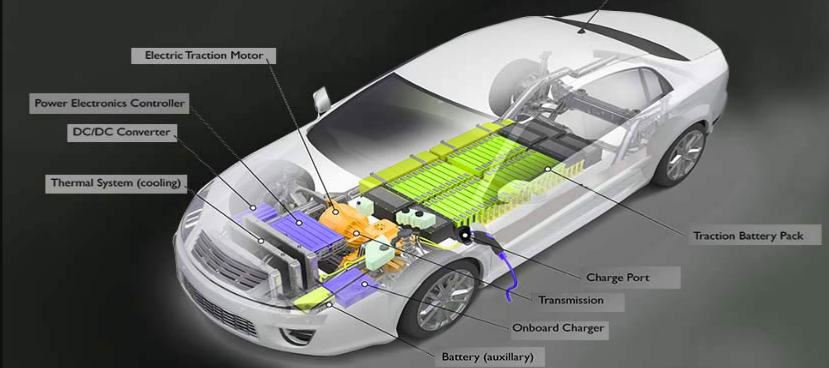
The working principle of an electric vehicle (EV) is quite different from that of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle. The primary components and the functioning of an electric motor are essential to understand the operation of an EV.

Basic Components of an EV
An electric vehicle consists of the following key components:
- Electric Motor: This is the heart of the electric vehicle. The electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to move the vehicle.
- Battery Pack: This is the energy storage component of the EV. The battery pack stores electrical energy and supplies it to the electric motor.
- Controller: This is the brain of the electric vehicle. The controller manages the power supplied to the electric motor from the battery pack. It regulates the speed of the motor by varying the voltage and current supplied to the motor.
- Charging System: This includes both the onboard charger and the charging station. The onboard charger converts AC electricity from the grid to DC electricity for charging the battery pack. The charging station supplies AC electricity to the vehicle.
- Transmission: Some electric vehicles have a single-speed transmission, while others have a multi-speed transmission. The transmission transfers the mechanical power generated by the electric motor to the wheels of the vehicle.
- Regenerative Braking System: This system converts the kinetic energy generated during braking into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery pack. This helps to increase the range of the electric vehicle.
Functioning of an Electric Motor
The electric motor in an electric vehicle works on the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday. This is the basic principle behind the functioning of an electric motor.
- Magnetic Field: The magnetic field in an electric motor is created by either permanent magnets or electromagnets (field windings) attached to the stator (the stationary part of the motor).
- Current-Carrying Conductor: The rotor (the rotating part of the motor) contains current-carrying conductors. When current flows through these conductors, they experience a force due to the magnetic field created by the stator.
- Rotation: The force experienced by the current-carrying conductors causes the rotor to rotate.
- Speed Control: The speed of the motor can be controlled by varying the voltage and current supplied to the motor.
The efficiency of an electric motor is much higher than that of an internal combustion engine, making electric vehicles more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Please note that this is a simplified explanation of the functioning of an electric motor. There are different types of electric motors, and their functioning may vary. For more detailed information, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on electric motors.
Gearbox in Traditional Vehicles
The gearbox is a crucial component in traditional vehicles powered by internal combustion engines. It plays a vital role in the vehicle’s operation by managing power and speed. Understanding the role of the gearbox and its different types is essential to appreciate the differences in the working mechanisms of traditional vehicles and electric vehicles.
Role of Gearbox in Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
The primary role of the gearbox in an internal combustion engine vehicle is to transmit torque from the engine to the wheels and regulate the power that the wheels get, depending on speed and load.
- Transmission of Torque: The engine of a traditional vehicle generates torque, which is a measure of rotational force. However, the engine operates within a range of speeds (RPM, revolutions per minute) and generates maximum torque only within a specific range of speeds. The gearbox helps in transmitting this torque to the wheels of the vehicle, making it possible to start, stop, and move the vehicle in different directions.
- Speed Regulation: The vehicle needs different amounts of power at different speeds. For example, it needs more power to accelerate from a stop or to climb a hill than it does to cruise at a constant speed. The gearbox provides this variable power by offering a range of gear ratios between the engine and the wheels. For instance, a lower gear ratio provides more torque but limits the maximum speed, while a higher gear ratio allows higher speed but provides less torque.
Types of Gearboxes
There are several different types of gearboxes used in internal combustion engine vehicles:
- Manual Transmission: This is the most traditional type of gearbox. The driver manually selects the gears by operating a lever connected to the transmission.
- Automatic Transmission: This type of gearbox automatically selects the appropriate gear based on the vehicle’s speed and the load on the engine. Automatic transmissions are easier to use and provide a smoother ride, but they are usually less fuel-efficient than manual transmissions.
- Semi-Automatic Transmission: This is a hybrid between manual and automatic transmissions. The driver can manually select the gears, but there is no clutch pedal. The transmission can also work in automatic mode, selecting the gears on its own.
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT): This type of transmission does not have fixed gears. Instead, it continuously varies the gear ratio, providing an infinite number of gear ratios between the minimum and maximum limits. CVTs provide smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency.
- Dual-Clutch Transmission: This is a type of semi-automatic transmission that uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets. This design allows faster gear changes and improves fuel efficiency.
For more detailed information on different types of gearboxes, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on gearboxes.
Each type of gearbox has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of gearbox depends on various factors like the vehicle’s purpose, the driver’s preferences, and the manufacturer’s design philosophy. In recent years, automatic transmissions, CVTs, and dual-clutch transmissions have become more popular due to their ease of use and fuel efficiency.

Necessity of Gearbox in Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles (EVs) have a different power and speed management system compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This difference raises the question of whether a gearbox is necessary in electric vehicles.
Power and Speed Management in EVs
Electric vehicles are powered by electric motors, which have a different torque and speed curve compared to internal combustion engines.
- Torque Curve: Electric motors can provide maximum torque right from the start and across a wide range of speeds. This characteristic eliminates the need for multiple gears to manage power and speed at different levels of engine load.
- Speed Range: Electric motors can operate efficiently over a wide range of speeds, which means they can handle both low-speed and high-speed driving without the need for multiple gears.
Due to these characteristics, many electric vehicles use a single-speed transmission, which does not have multiple gears like a traditional gearbox. Some high-performance electric vehicles use a multi-speed transmission to achieve higher top speeds or improve efficiency, but this is the exception rather than the rule.
Comparison with Traditional Vehicles
In traditional vehicles, the internal combustion engine operates efficiently only within a narrow range of speeds and generates maximum torque within a specific range of speeds. This necessitates a gearbox with multiple gears to manage power and speed at different levels of engine load and vehicle speed.
In contrast, electric vehicles do not have this limitation because electric motors can operate efficiently across a wide range of speeds and provide maximum torque right from the start. This eliminates the need for multiple gears to manage power and speed, which is why many electric vehicles do not have a traditional gearbox.
Evolution of Electric Vehicle Technology
The technology behind electric vehicles (EVs) has evolved rapidly in recent years, making them more accessible and attractive to consumers. The advancements in electric motors and innovations in vehicle design are two key areas that have contributed to this evolution.

Advancements in Electric Motors
Electric motors are the heart of electric vehicles, and their development has played a crucial role in the evolution of EV technology.
- Higher Efficiency: Modern electric motors are incredibly efficient, often converting over 90% of electrical energy into mechanical energy. This high efficiency contributes to the overall energy efficiency of electric vehicles and helps to maximize their range.
- More Power: Advances in materials and design have led to electric motors that are more powerful and compact. For example, the use of rare-earth magnets and high-performance winding materials has helped to increase the power density of electric motors.
- Better Cooling: Efficient cooling systems have been developed to manage the heat generated by electric motors. This has helped to improve the performance and longevity of electric motors.
- Regenerative Braking: This feature allows electric motors to act as generators during braking, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy and storing it in the battery. This helps to increase the range of electric vehicles and improve their overall energy efficiency.
For more detailed information on electric motor advancements, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on electric motors.
Innovations in Vehicle Design
Vehicle design has also evolved to accommodate the unique characteristics of electric vehicles.
- Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials such as aluminum and carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers has helped to reduce the weight of electric vehicles, which in turn helps to increase their range.
- Aerodynamic Design: Electric vehicles are often designed with aerodynamics in mind to reduce air resistance and improve energy efficiency. For example, many electric vehicles have a streamlined shape and smooth underbody to minimize drag.
- Battery Integration: The design of electric vehicles often incorporates the battery pack as a structural element, which helps to improve the vehicle’s rigidity and reduce its weight.
- Improved Safety Features: Electric vehicles are designed with various safety features such as thermal management systems for the battery pack and reinforced structures to protect the battery in case of a collision.
For more information on innovations in vehicle design, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on electric vehicle design.
These developments have helped to make electric vehicles more efficient, powerful, and safe, contributing to their growing popularity and adoption.
